What Is the Predominant Export Destination of West African Art? Quizlet
6.2 Urban North and Andean Due west
Learning Objectives
- Understand the dynamics of Venezuela's urban society and why Venezuela has not experienced a robust rural-to-urban shift to the extent that other countries have.
- Summarize the production of the three main export products of Colombia and explain the United states of america role in their export.
- Compare the three master countries in the Andean West region of S America and empathize how they gained their wealth and who has benefited the almost over the years from that wealth.
- Outline how Paraguay'southward geographical setting has allowed it to gain wealth and provide opportunities for its people.
Venezuela: Oil, Politics, and Globalization
Bordering the Caribbean area is the large urban country of Venezuela. The Andes Mountains attain into the northern role of the land and make up the terrain of the northern coastal region all the way to the capital city of Caracas. The large grassland plains of the Llanos extend further due south from the Colombian border to the Orinoco River delta. The Llanos is a big, sparsely populated region that makes upward about one-3rd of the country. Information technology is remote, susceptible to flooding, and used mainly for raising cattle. In the southeast of Venezuela are the Guiana Highlands, which make for a spectacular physical landscape of tropical forests and rugged mountainous terrain. The highlands include Angel Falls, the tallest waterfall in the world. Angel Falls drops two,647 feet and is Venezuela'southward well-nigh popular tourist allure. Lake Maracaibo, a big inland body of water located in the western region of the country, is not a true lake in that it is open to the Caribbean area Bounding main, but it is considered the largest inland trunk of water in Due south America. Lake Titicaca, located in the Andean region of the Altiplano on the edge between Peru and Bolivia, is considered the continent's largest freshwater lake.
Figure 6.14 Northern South America and Venezuela
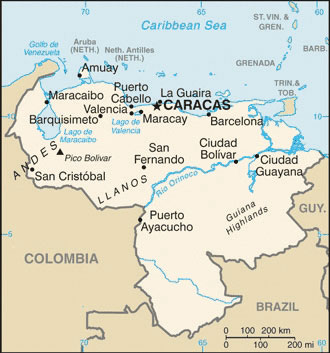
Notice that most of the primary cities are located forth the northern coast.
Figure half dozen.fifteen Affections Falls, Venezuela
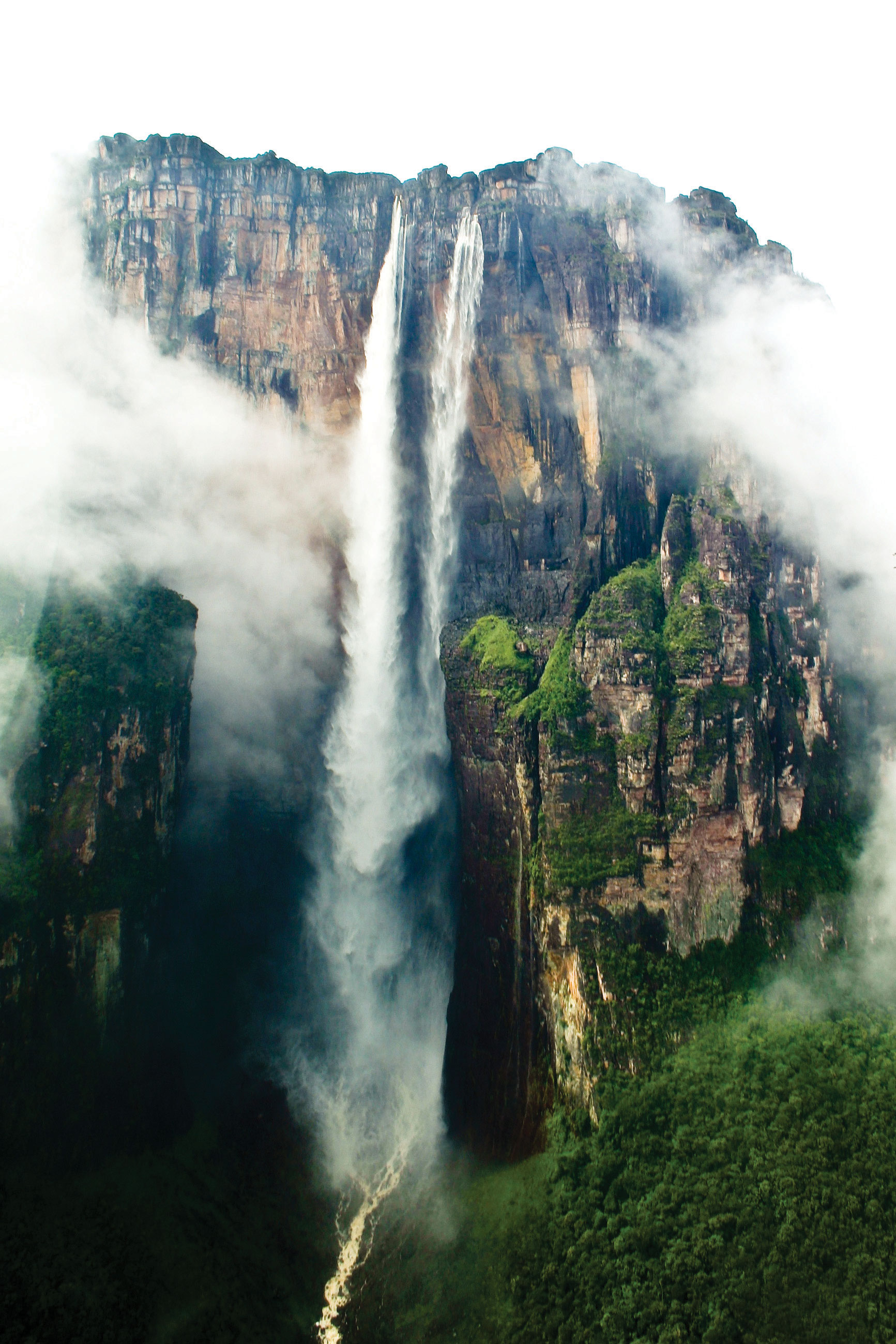

The total falls is estimated at 3,212 feet; the largest free fall is estimated to be about 2,647 feet—well-nigh half a mile. Angel Falls is the land's number one tourist attraction.
Venezuela has an assortment of physical regions, but well-nigh of the population lives along the northern coast. Most xc percent alive in urban areas, and the capital Caracas has the highest population. Less than 5 per centum of the population lives south of the Orinoco River, and Amerindian groups live in the interior and forth the river.
Included in the Mixed Mestizo Cultural Region, Venezuela has a heavy Castilian influence laid over an Amerindian base in a plantation region known for its African infusion. In that location is also a potent Caribbean cultural flavor, which is evident in the region'southward music and lifestyle. The official language is Spanish, only more than thirty ethnic languages are still spoken in the land.
Venezuela gained its independence from Spain in 1821 and has developed into an urban country with an economy based on oil product. A large extent of the interior is undeveloped. Venezuela does not have extensively developed agricultural production, and so nearly food goods are imported. Lake Maracaibo has vast oil reserves below it that have provided substantial wealth to the country.
Equally much as xc percent of Venezuela's consign earnings are from the export of oil. Venezuela's national oil company, CITGO, has made extensive inroads into the The states gas station market place. The country was one of the founding members of OPEC (System of Petroleum Exporting Countries), which is ordinarily associated with the oil-rich states of the Western farsi Gulf. In the past decade, Venezuela has been ane of the top five countries exporting oil to the United States. The other 4 are Canada, United mexican states, Saudi Arabia, and Nigeria.
As is the case with many countries, national wealth in Venezuela does not filter downwardly to most of the population. The wealthy elite who have benefited the about from the nation'due south wealth often detect themselves on the opposite side of the political debate from the majority, who are probable to alive in poor conditions. Caracas has many upscale neighborhoods, but it likewise has a large number of slums on the outskirts of the metropolis. Slums in S America go by different names, such as barrios in Venezuela or favelas in Brazil. Many of Venezuela'southward barrios are built on the mountainsides of the Andes.
Figure half-dozen.16 The Two Sides of Caracas, the Upper-case letter Metropolis of Venezuela
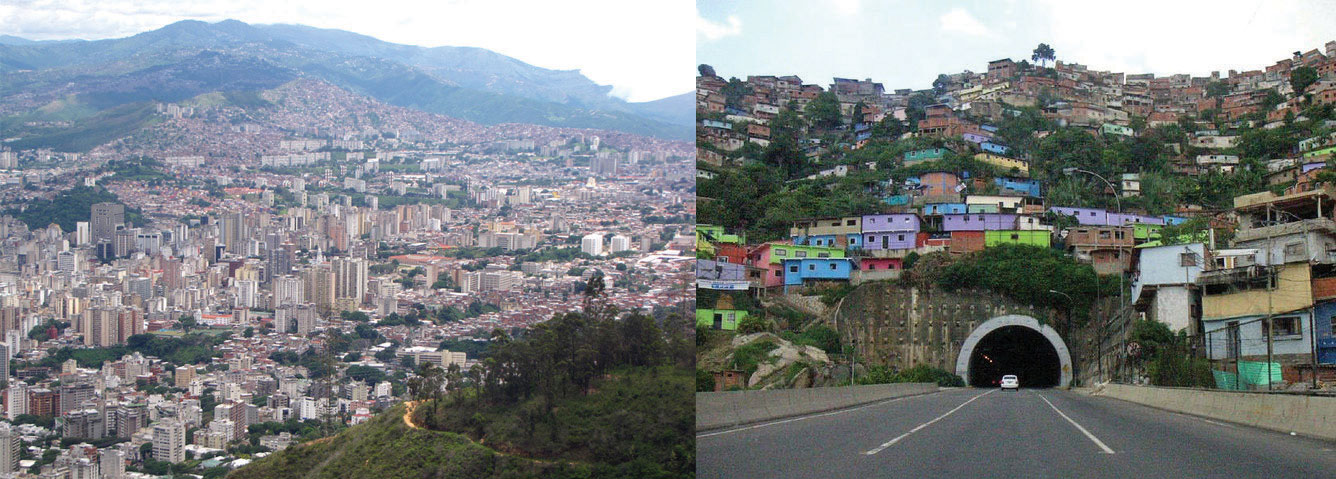

The photo on the left is of the main urban core, with upscale neighborhoods. The photo on the right is a barrio located on a steep mountainside. Barrios are usually cocky-constructed slum areas and are like to favelas in Brazil.
Exporting oil to the Us does non inherently pb to a friendly political human relationship between the United States and Venezuela. There has been some political unrest inside the country related to the electric current president, Hugo Chavez, holding continuous terms in function without term limits. President Chavez has held close ties with socialist Cuba and with the Castro government and has fabricated somewhat combative statements virtually the globe's core economic countries. From time to time, his rhetoric and his positions are not geared toward enhancing the land's political human relationship with the U.s.. This situation has caused concern within the US political establishment with regard to the position that the United states takes toward Venezuela. Yet, the United States remains Venezuela's number i trading partner in both imports and exports.
Politics in Venezuela often plays the wealthy elites against the poorer bulk, and President Chavez has non been an exception. Chavez has supported socialist political leaders from other Latin American states and has pushed a globalization agenda along the aforementioned lines. The country'southward enormous oil revenues and its current political climate take increased Venezuela'south visibility in the global arena, just how this will play out over the long term is unclear. In the past, Latin America has had a greater number of elected political leaders with more progressive or socialist views. These trends proceed to shape the economical trade agreements between countries. Venezuela has been working to increase sales of oil to countries in Mercosur (the Southern Cone Common Market place), which is the most significant trade association in South America.
Globalization is also evident in Venezuela'southward cultural and social dynamics. In many Latin American countries, soccer (European football) is the about popular sport, but Venezuela's biggest sport is baseball game because of the influence of early U.s.a. activity in the land's oil industry. Soccer is gaining attention and support, however. Orchestras and classical music performances have also gained notoriety in recent years. Concert halls from the Americas to Europe have experienced the performances of the Simón Bolívar Youth Orchestra. The Miss Venezuela pageant is a major product for the country, and Venezuela has won the tiptop title at least v times in each of the following pageants: Miss World, Miss Universe, and Miss International.
Republic of colombia: Drugs, Coffee, and Oil
Three ranges of the Andes Mountains run from north to southward through Republic of colombia, which is larger than the nine almost southeastern Us states. With a country area covering about 440,839 square miles, Colombia is more than 10 times larger than the U.s.a. state of Kentucky and close to twice the size of France. Colombia borders five countries, with the Caribbean to the northward, the Pacific Bounding main to the west, the Orinoco River to the due east, and a brusque segment of the Amazon River to the far due south. Even though agriculture has been a mainstay of the state'southward economic activities, because of the influence of the mountainous terrain, about 75 percent of the population lives in urban areas.
Figure 6.17 Concrete Size of Colombia: 440,839 Square Miles
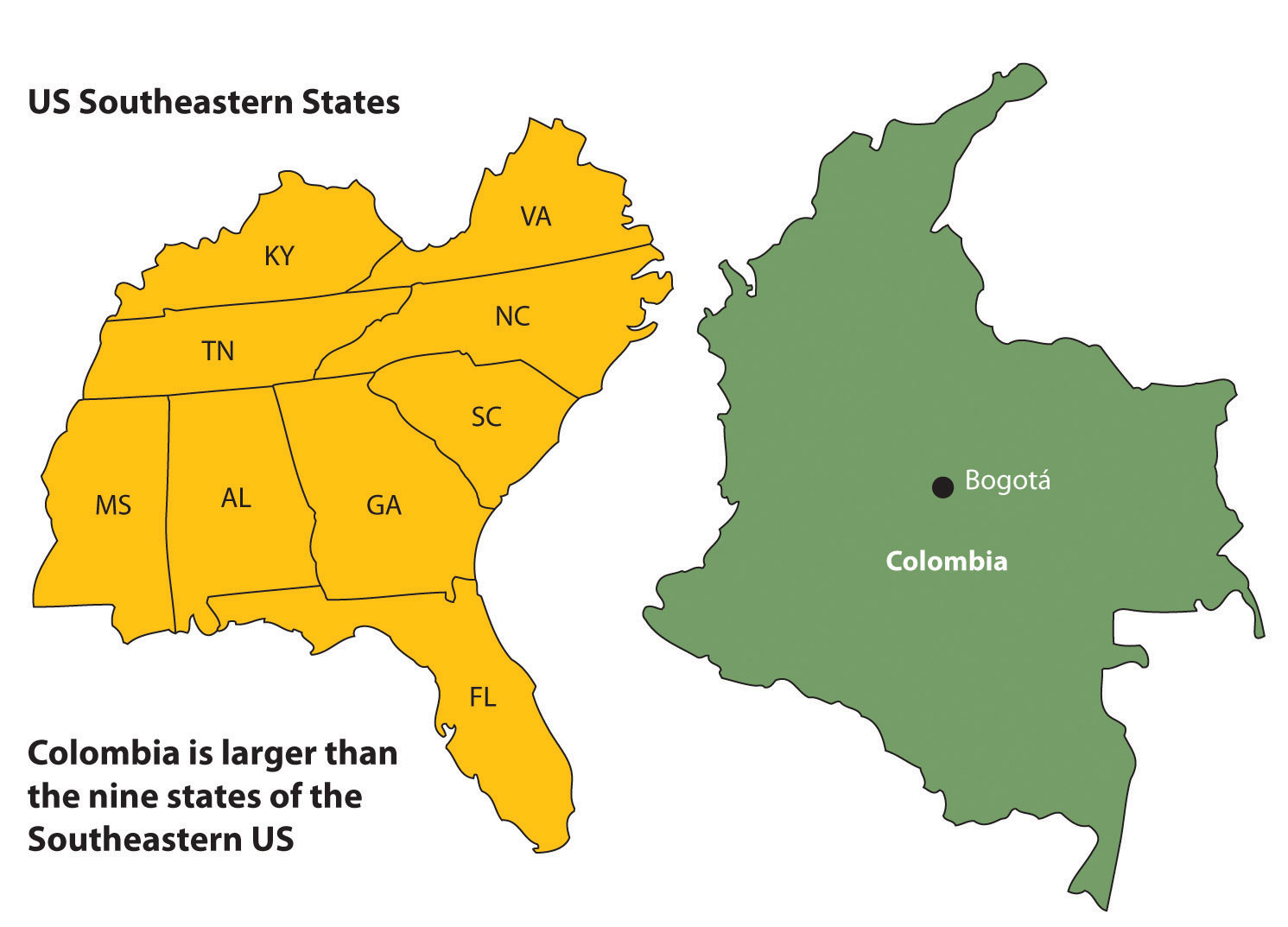
Republic of colombia was a Spanish colony during the time that Spain controlled most of western South America. Colombia became independent in 1819. The region of Panama, which was showtime a function of Republic of colombia, bankrupt away in 1903 when the United States backed Panama's independence movement. Afterwards Colombia became independent of Spain, the conservatives (wealthy elite) and the liberals (poor workers) struggled to gain control of the government. Since 1948, the disharmonize, known as La Violencia, has caused more than 2 hundred thousand casualties. During the twentieth century the government in Republic of colombia has not always been peaceful or stable. By the showtime of the twenty-showtime century the authorities has become more unified and the state has even witnessed an increase in tourism.
Colombia and the Drug Merchandise
Republic of colombia's tropical climate and its many remote areas contributed to its development as a major coca-growing region. By the 1970s, all-encompassing drug smuggling had developed, and powerful drug cartels became major political brokers within the state, competing against the government for command of Colombia. The largest and most organized cartels operated out of Medellin and Cali, the second- and 3rd-largest cities in the country after the capital urban center of Bogotá.
The coca plant grows throughout the slopes of the Andes, from Colombia to Bolivia. Historically, locals have chewed it or brewed it into tea. Coca can alleviate height sickness and act as a mild stimulant. Using modern methods and potent chemicals, the coca leaves can be converted into coca paste and then into cocaine hydrochloride, a powerful narcotic. It often takes upwards to a ton of such chemicals as sulfuric acrid, kerosene, methyl alcohol, and additional substitutes to produce a kilo of cocaine. Once the process is completed, most of the chemicals are discarded and frequently find their style into nearby rivers and streams, which are the same water supplies that local people drink, clean with, and bathe in. Birth defects have become a trouble in coca-growing regions considering of the loftier levels of chemic pollution in water supplies.
It must be noted that the brusque, leafy coca plant that cocaine comes from is non the same as the cacao tree that produces the beans that chocolate or cocoa comes from. They are two completely different plants with separate processes.
The U.s. is the largest cocaine market. Clandestine airfields and private boats send the cocaine from Colombia to distribution centers in Mexico, Central America, or the Caribbean area. From there, the drugs are smuggled into the United States. Colombian drugs are a multibillion-dollar manufacture that makes up a large portion of the Colombian economic system. The event of the drug industry on the people of Colombia is extensive—from the gunfire on the streets to the abuse of government officials. In recent years, the same drug cartels that take operated the cocaine industry have imported opium poppies, which grow well on the college and more than arid slopes of the Andes. Opium poppies are native to Asia but have been transported to South America. Opium is extracted from the seedpod and can be further refined into heroin. Colombian drug cartels, with a Mexican distribution network, have muscled into every bit much every bit 20 percent of the US heroin market. The U.s. regime has supported the Colombian authorities in the fight confronting the drug cartels and the trafficking of illegal drugs out of Republic of colombia.
Colombian Java and Oil
Republic of colombia'southward two primary legal exports to the The states are coffee and oil. Java is only grown in the tropics, since coffee copse must be grown in a frost-free environment. Coffee trees, which originally grew in Ethiopia, have since been grown throughout the world. Java trees can grow in elevations from body of water level to six thousand feet, but nigh of the all-time specialty coffee is grown at elevations between 3 thousand to six 1000 anxiety. Colombia has ideal weather for growing java and was one time the world's largest coffee producer; at present Brazil and Vietnam each produce more.
Early coffee production in Colombia was initially promoted by Catholic priests who were influential in supporting local parishioners to grow the crop. The manufacture was profoundly enhanced in 1927 with the germination of the National Federation of Coffee Growers of Republic of colombia. Coffee product on the mountain ranges of the Andes in Colombia supports up to a half million small farms and local growers that make up a large portion of the coffee economy. Harvesting coffee is labor intensive and tin can employ large numbers of workers. The seasonal nature of the harvest also leaves workers to find employment during the rest of the growing season.
In contempo years, there has been growing concern near how climatic change will go along to bear on the region's coffee production. In the past century, parts of Republic of colombia experienced upwardly to a 1 ºC boilerplate temperature increase and upwards to a 25 percent increase in atmospheric precipitation. These climate changes have negatively affected java output and reduced coffee production as much every bit 25 percent in some areas. New agronomical methods are beingness developed in an try to counter these effects.
Oil has at present get Colombia's number i legal export. Oil is constitute in fields in the northern and central regions of Colombia. Immense quantities of coal are also establish in the aforementioned regions, simply oil is more valued on the export marketplace. Pipelines connect the interior oil fields of Colombia with the northern ports. The U.s.a. marketplace size and population make information technology the globe'south largest oil consumer. US oil companies have been investing in the development of Colombian oil for many years. Colombia has been a developing oil source even though its total extractable resources are not as vast as in other countries. For case, in 2006 the United States imported more oil from Republic of colombia than from Kuwait, Oman, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), Bahrain, Qatar, and Yemen combined.
Figure half dozen.eighteen Insurgent Areas
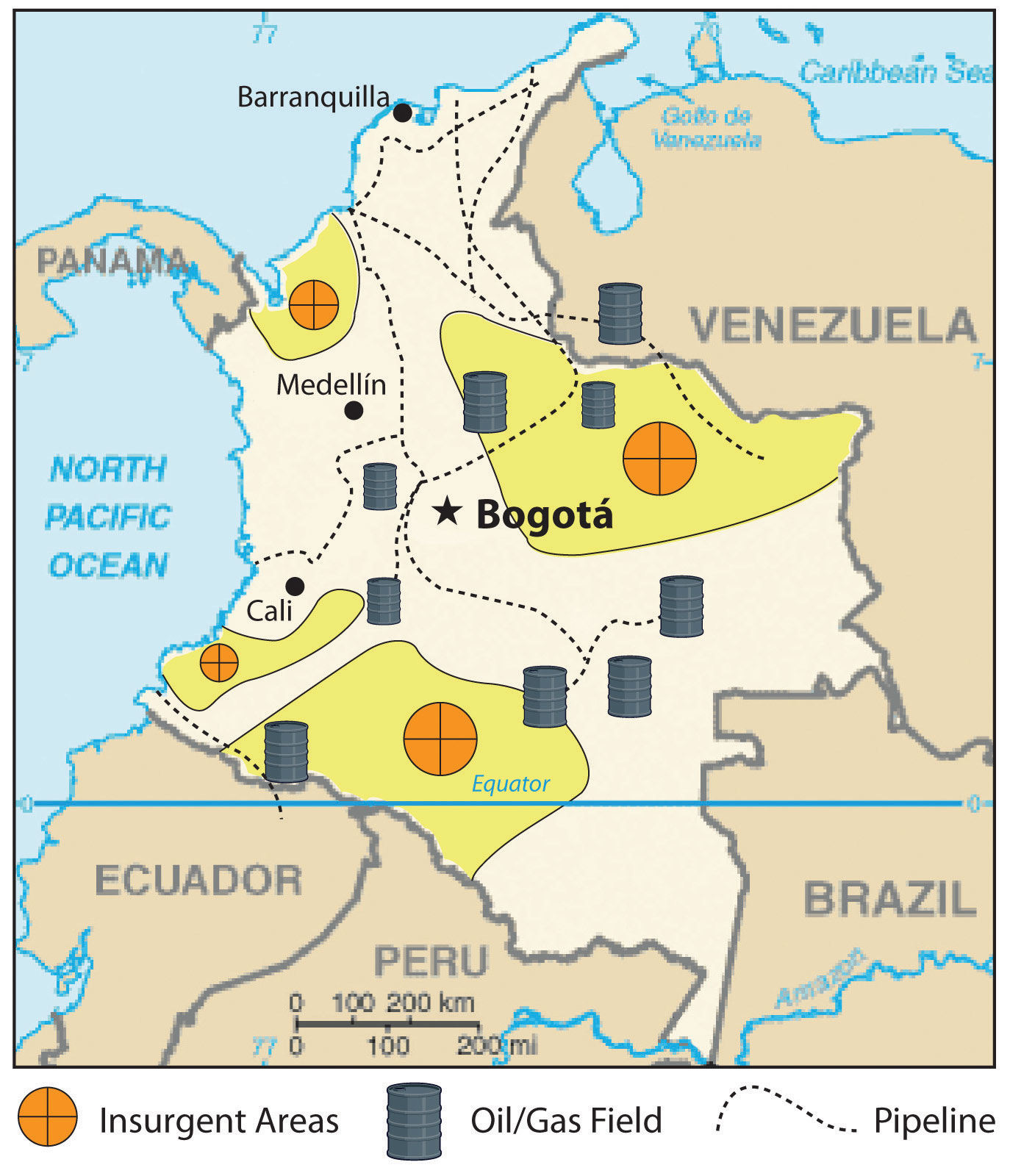
Insurgent groups control regions in Colombia equally large as US states.
CIA World Factbook – public domain.
Since the United States is the largest consumer of Colombian oil, it is easy to understand why the United states has a vested interest in the stability of the Colombian government. A sizable portion of Colombia is controlled not by the government but by drug cartels or other insurgent groups. Dozens of guerilla organizations also control portions of Colombia. Some insurgent groups support the government and are against the drug lords, while others fight the government and work independently or with the cartels. Drug sales, kidnappings, and extortion of legitimate businesses provide income to these groups. Thousands of children serve in these groups, and near a third of them are female. The virtually powerful insurgent group is FARC (Revolutionary Armed forces of Colombia), which controls entire regions the size of many United states of america states. FARC is a recognized political entity past neighboring countries only is non given the same recognition by the U.s. and many external countries of the region.
Effigy 6.19 Colombian Exports

The 3 master export products of Colombia are illegal drugs, oil, and coffee. The Us is the largest consumer of all three.
The relationship between Republic of colombia and the Usa is often conflicting. The U.s. consumer supports the Colombian drug cartels by beingness the largest consumer of illegal drugs. The US government, under the Drug Enforcement Assistants (DEA), has alleged a war on drugs and has supported the Colombian government with billions of dollars in foreign aid to fight that war. On another front, The states oil corporations have paid insurgent groups to protect their oil assets. Oil is exported to the United States, bringing billions of dollars into the Colombian economy. The chaos in Colombia is directly related to the exploitation and marketing of their resource. It is the people of Colombia that endure in the cross fire from this civil war of corruption, criminal offense, decease, and destruction. The U.s. is a counterforce partner in this situation but operates from the consumer end of the resource pipeline. The largest consumer market place for Colombia'south export of oil, drugs, and coffee is the United States, which is also the largest contributor of foreign help to Republic of colombia.
Rural Amerindian States of Republic of ecuador, Peru, and Bolivia
The Central Andes, which includes Ecuador, Republic of peru, and Bolivia, were abode to the Inca Empire. The empire had gone through some internal divisions and was working on unifying the region when Francisco Pizarro's small army defeated the Incan warriors and brought near colonial rule first in the 1530s. Many cultures lived in the Cardinal Andes before the Inca, and their legacy continues in the customs and the ways of the Amerindian people who however live there today. Castilian is the official language, or the lingua franca, but indigenous languages are widely spoken and dominate in the rural areas and remote villages. Republic of ecuador, Republic of peru, and Republic of bolivia make up the core of the Rural Amerindian Region of South America. There have been border disputes amongst the three countries, and likewise with their neighbors. Nevertheless, they all share the Andes and have many things in common.
Figure vi.twenty Machu Picchu
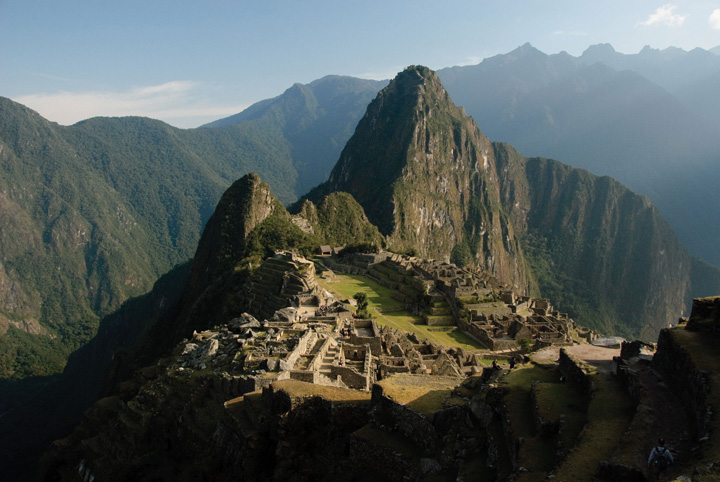

High in the Peruvian Andes, the Lost City of the Incas, Machu Picchu, was rediscovered in 1911 by Yale archaeologist Hiram Bingham and is one of the most beautiful and enigmatic aboriginal sites in the world. The ruins are located at well-nigh seven,970 feet in elevation and are surrounded by higher peaks of the Andes.
Physical Geography
The physical geography of the Fundamental Andes includes more than but the high Andes Mountains, although they boss the landscape. The coastal region to the westward of the Andes is more often than not warmer than the cooler climate of the mountains. The equatorial region is rather boiling. The coastal region in southern Peru is dry out and barren considering of the sea currents and the rain shadow issue of the Andes, which creates the Atacama Desert that extends up from northern Chile. Southwest Bolivia has some of the world'south largest salt flats in this dry out and arid region. In the interior, on the eastern side of the mountain ranges, is the huge expanse of the Amazon Basin. Tropical and humid with heavy atmospheric precipitation is generally the climate rule. Rain forests and jungle fauna can exist found on the eastern slopes. The Altiplano region has the high-elevation Lake Titicaca. The variations in physical terrain provide extensive biodiversity in animal and found species. Information technology besides supports a variety of economic activities to exploit the bountiful natural resources.
Even though the Altiplano region borders the Pacific Ocean, it also links directly to the Atlantic Ocean. The headwaters that create the Amazon River start in Peru, and by the time the h2o reaches the Peruvian urban center of Iquitos, the river is large enough to accommodate large aircraft vessels. Iquitos is a port city for the Atlantic Bounding main with access to Europe, Africa, or eastern North America. The port also links the region with Brazil's gratuitous-trade zone in Manaus, which has admission to large oceangoing shipping and an international market.
Economic Geography
The region'south main income comes from exports of minerals, fossil fuels, and agricultural products. Oil is the number i means of gaining national wealth in Ecuador and Republic of peru; natural gas is the number one consign of Bolivia. Gold, silver, can, and other minerals are likewise arable and are being exploited as conditions allow. The Spanish opened up a large silver-mining operation in Potosí, Bolivia, which continues to be exploited with modern mining methods. Potosí, 1 of the earth's highest-superlative cities at xiii,420 feet above sea level, was once the largest silver mine in the world.
The metropolis of Lima, Peru, was built on wealth from gold and silverish extracted from the Inca Empire and the Andes Mountains. Equally is the case in many peripheral regions, the economical country of Republic of peru, Republic of ecuador, and Bolivia is dependent on global prices for their export products. There has been considerable conflict and political wrangling about who controls the wealth from extractive economic activities. Originally, the Spanish conquistadors took the materials and the wealth. They were replaced by Mestizo land owners and wealthy elites who struck deals with international corporations. The corporations exploited the countries' natural resources, with little turn a profit actually catastrophe upward in the hands of nearly of the people. These issues remain at the tiptop of the political agendas in all 3 countries.
Effigy 6.21 Quito, Ecuador
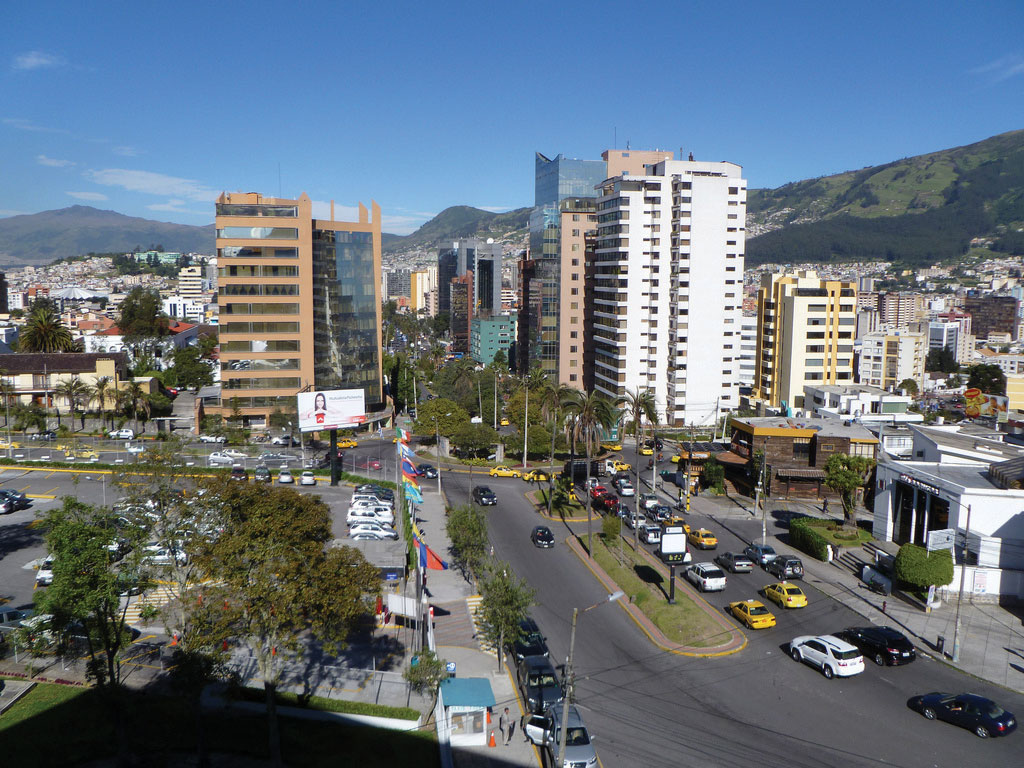

Quito, Ecuador, is an urban center high in the Andes, with a population of more 1.five million. This photograph shows the big buildings of the central business organisation district with the mountains in the background surrounding the city. Quito is at about 9,200 anxiety in elevation and is considered the 2d-highest-tiptop capital in the world after La Paz in Bolivia.
Poverty and the exploitation of natural resource usually outcome in environmental deposition unless proper measures are taken to forbid it. The area's heavy reliance on oil and gas extraction to gain national wealth has come at a great cost to their environment. Many oil spills take caused oil to enter the freshwater supplies of local residents and pollute the rivers and streams of the Amazon Bowl. Mining has traditionally devastated the land considering large portions of globe are removed to extract the ore or mineral. Pollution is causing a loss of habitats and destroying ecosystems, and few measures are being taken to forestall information technology. Deforestation is being caused by the timber manufacture and by clearing for agriculture. Overgrazing and the removal of the trees exit the soil open to erosion.
Tourism
Tourism is expanding to connect travelers with opportunities to explore Incan and pre-Incan sites, which are the principal attractions. One of the main tourist attractions in Republic of peru is the aboriginal city of Machu Picchu in the Andes non far from Cuzco. In 2010, Peru gained over two billion dollars from the tourist activities of about two million foreign tourists (Andina). Ecuador's major tourist attraction is the Galapagos Islands, which aided Charles Darwin in understanding natural selection and the evolutionary process. Republic of bolivia has a number of aboriginal sites that predate the Inca and have become major tourism destinations. The aboriginal city of Tiahuanaco and the enigmatic Lake Titicaca are proficient examples.
Tourism can be a great source of economic income but it can come at a cost to the environment. There is always concern that loftier-traffic tourism sites similar Machu Picchu can be degraded by the sheer mass of people visiting the site. The environmental banner may be all-encompassing. The term ecotourism has been used to point the activeness of people traveling to feel and enjoy the natural world with an aim not to harm the environment in the process. The main objective was to make the tourism activity sustainable, which promoted stewardship of the land and respect for its attractions. Jonathan Tourtellot, director of the National Geographic Society's Center for Sustainable Destinations, coined and prefers the term geotourism, which can be translated every bit the stewardship of place and the preservation of its essential graphic symbol (Miller-McCune). These concepts are becoming more integrated with the tourism industry to promote a sustainable model for loftier traffic sites like the Galapagos Islands with frail ecosystems.
Political Issues
Economics usually bulldoze politics. Appropriately, Peru, Ecuador, and Bolivia have endured some serious ups and downs in their political environment. Corruption, authoritarianism, and human rights violations have been mutual accusations toward the political leadership of the countries. To accost the economic status of his country in 2000, Republic of ecuador's president appear that the state would adopt the US dollar as its chief medium of substitution. This may accept brought some economic stability, but information technology did not address the problems of a loftier national debt and a fluctuation in article prices. All three countries accept undergone political turmoil. Big percentages of the populations alive in poverty. Republic of bolivia is considered one of the poorest countries in South America. In 2006, Bolivia elected a socialist president from the MAS (Movement for Socialism) political party who was from a minority Amerindian grouping rather than a member of the wealthy aristocracy. In Peru, a number of presidents have been forced to resign, and military machine coups accept too produced leadership changes.
Figure 6.22 Indigenous Women on Their Way Abode from the MAS congress in Bolivia, January 2009
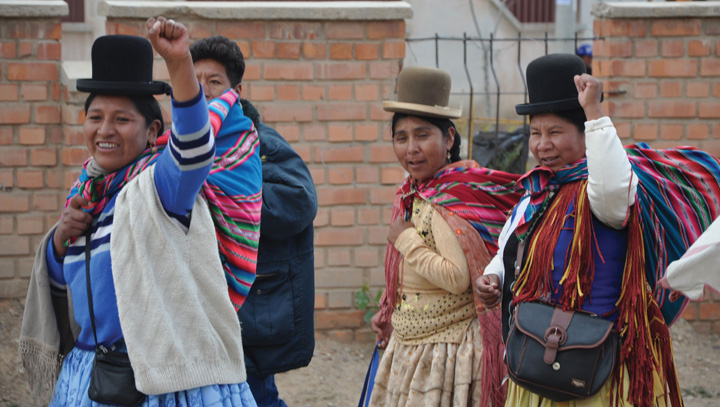

MAS is the Move for Socialism, which has been active in Bolivian politics.
Population and Culture
Population growth is a major factor in the future of Peru, Ecuador, and Republic of bolivia. In 2010, Bolivia had more than ten million people, Ecuador had more than than fourteen million, and Peru had about twenty-nine 1000000. More than 30 percent of the population of Ecuador and Bolivia resides in rural areas and make a living from subsistence agriculture. All three countries have large populations in relation to the production of acceptable food. Peru and Bolivia are large countries in physical area merely practise not have a loftier per centum of arable land. Rural-to-urban shift is increasing and the major cities are standing to expand, overtaxing public works and social services.
The civilization of the Central Andes is heavily influenced by its rural Amerindian heritage. The foundation of the traditional agrarian gild has been subsistence agriculture. Ane-3rd of the population in Ecuador and Bolivia and up to one-fourth of the population in Peru go along to live a traditional way of life. Local cuisine reflects the connection to the land. Potatoes, maize, guinea pigs, and fish are common fare in rural areas. The cities are encountering international influences that are changing the demands in local cuisine and culture. Traditional food, arts, and local crafts still thrive in the local districts and for the tourism marketplace.
Figure 6.23 The Andean W and Paraguay
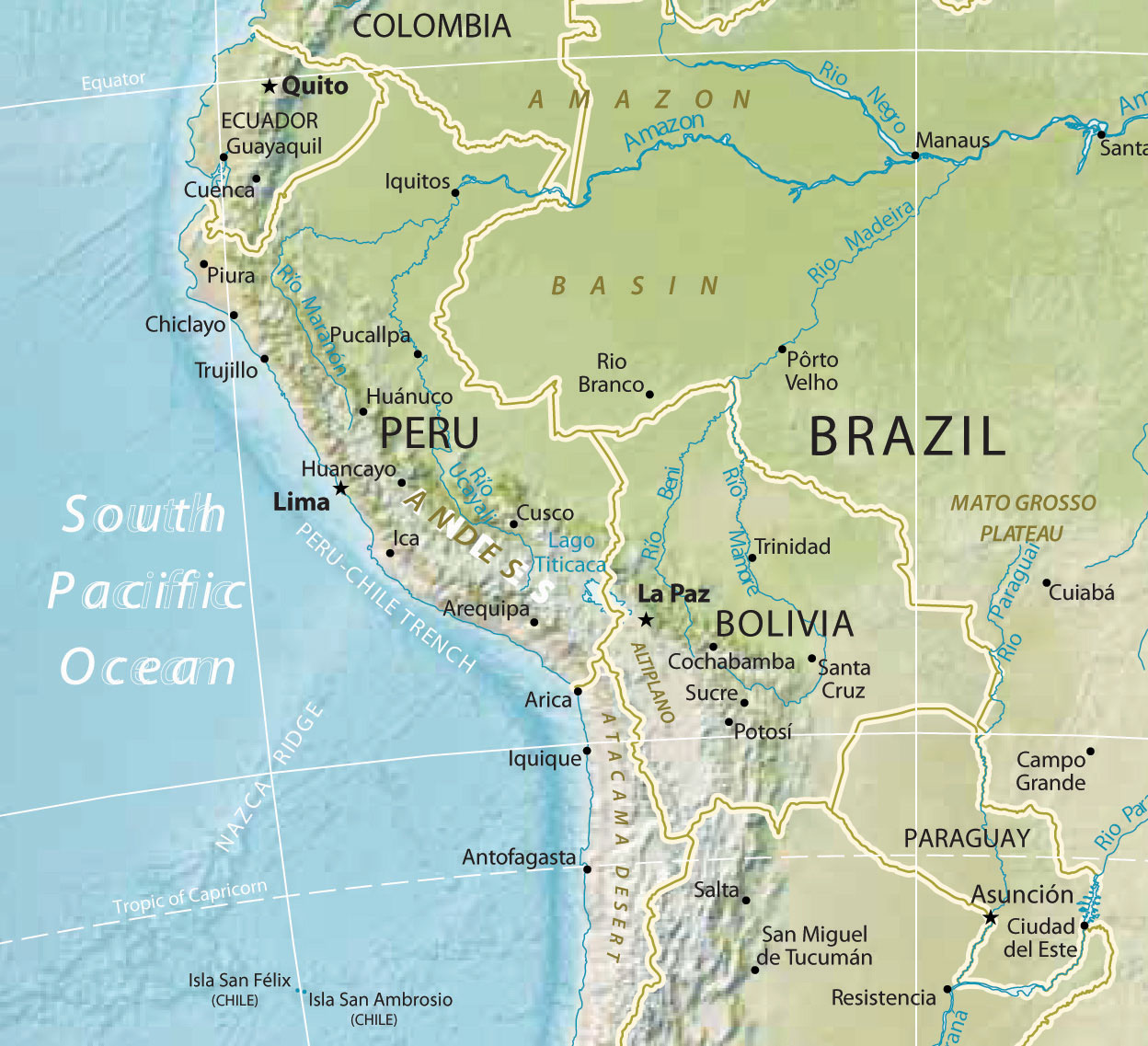
This map also displays a part of the Amazon Basin, the Atacama Desert, Altiplano, and the Mato Grosso Plateau.
This region'due south location on the Pacific Rim of South America has contributed to an Asian influence, which has integrated itself with the local culture. Erstwhile president of Peru Alberto Fujimori had Japanese ancestry and held dual citizenship in both Peru and Nihon. Similar to Havana, Cuba, in Middle America, Lima, Peru, is likewise home to one of the primeval Chinatowns in the Americas, where the Chinese civilization has mixed with the Latino culture to create a unique cultural blend. Bolivia is landlocked and does not have the advantage of a west-coast port city to interact with the Asian marketplace. Still, its civilization is still impacted by globalization and is evolving from within.
Paraguay
Paraguay is located in the Mixed Mestizo Cultural Region betwixt Brazil, Argentina, and Republic of bolivia. This landlocked state is not located in the Andes. The state's poor economic characteristics and troublesome political dynamics are similar to those of its neighbors in the Central Andes. Like other Latin American countries, most of the population practices Catholicism. Spanish is one of the main languages along with Guarani, the local linguistic communication of the people. The country's proper noun comes from the Paraguay River, which flows through the region and provides hydroelectric dams that provide all the electricity for the country. Paraguay suffers from a lack of infrastructure. The government has not been able to provide for the needs of a growing population with a fertility rate of more than than three children per family.
As much as 40 percent of the population makes its living from agriculture. Nevertheless, weather in the rural areas are poor: less than 10 percent of the land is abundant. There is not much agricultural growth that could heave the economy. Paraguay is the 6th-largest producer of soybeans in the world, and cattle ranching is its other strong commodity. A large portion of the marshlands have been transformed for agricultural purposes, merely this has caused a loss of wetlands as a habitat.
The economy is afflicted by poverty and an absenteeism of opportunities and advantages. Connections to global markets are hindered by the lack of an international port. Corruption and unstable governments are the political system'southward legacy. There is a wide disparity between the social elites, who own a loftier percentage of the land, and well-nigh of the population, which remains in poverty with poor living atmospheric condition. Large family size and rural-to-urban shift has caused rapid growth of the urban areas. Sixty percent of the population lives in the cities, and they ofttimes suffer from insanitary conditions because of water pollution. The largest slums in the country are found in the area of the capital city of Asuncion, which has almost two 1000000 people. In the urban areas, at that place is a strong informal market place economic system that thrives on imported goods being redistributed to other countries, but at that place is no formal tape-keeping system. An enormous number of black-market goods are brought in and resold to neighboring countries such as Brazil and Argentina, its two largest trading partners. In such conditions, crime and illegal activities thrive, and the rule of law is difficult to enforce.
Key Takeaways
- Most of the people in Venezuela live in cities along the Caribbean area coast. The land has always been urban and has non developed its agricultural production. Venezuela depends on oil exports to gain near of its national wealth.
- The U.s. is the largest consumer of products exported from Republic of colombia. Illegal drugs, oil, and coffee and are the three main export products of Republic of colombia. The United states direct or indirectly supports the 3 chief factions vying for power inside Republic of colombia.
- The Andean countries of Ecuador, Peru, and Republic of bolivia share like developmental dynamics, including a big percentage of Amerindian people and reliance on the consign of natural resources to proceeds national wealth. The wealth gained from exports is concentrated in the hands of elites rather than filtering down to most of the people.
- Paraguay is a landlocked country between the Andes and the Atlantic declension. It is a poor nation with few opportunities to advance its standard of living. The country has been a main staging ground for unregulated goods to exist redistributed throughout the region.
Discussion and Study Questions
- How intense is the current rural-to-urban shift in Venezuela? What accounts for this unique situation?
- What are the 3 main export products of Colombia? How is the United States involved in each of them?
- Why is coffee non grown in the continental United States? Where are the main types of coffee grown?
- What three groups vie for control of the diverse regions of Colombia? How does the Usa directly or indirectly support all three groups?
- What ecology problems result from the cocaine product process?
- How did colonial activeness assist in determining which indigenous group or groups would be at the top or lesser of the socioeconomic hierarchy in the Andean Due west region of South America?
- What are some of the common difficulties with the political systems of the countries in the Andean Due west?
- What does Paraguay have in common with Bolivia? How have the 2 countries each addressed this mutual state of affairs?
- Where has socialism been promoted or supported in the countries of South America?
- What types of agriculture are establish in the northward and western regions of South America?
Geography Exercise
Place the following central places on a map:
- Angel Falls
- Machu Picchu
- Pacific Rim
References
Andina, "Peru's Inbound Tourism Revenue to Attain $two.ii Billion This Year," http://www.andina.com.pe/ingles/Noticia.aspx?id=nfbX5vudSxw=.
Miller-McCune, "Can Tourism Be Sustainable?," http://www.miller-mccune.com/environment/can-tourism-be-sustainable-16362/.
martinezhoppled77.blogspot.com
Source: https://open.lib.umn.edu/worldgeography/chapter/6-2-urban-north-and-andean-west/
0 Response to "What Is the Predominant Export Destination of West African Art? Quizlet"
Post a Comment